On May 22, 2018, the “Key Technologies and Applications for Mass Manufacturing of Large-Size High-Performance Laser Neodymium Glass” project hosted by ZKSH Opto-Mechanical Technology Corporation won the second prize of China's National Technology Invention.
The laser inertial confinement fusion device is one of the two technological paths to achieve controllable nuclear fusion, which is of great national strategic significance. The core material of this device-the continuous melting technology of laser neodymium glass is recognized as one of the most difficult optical functional glass preparation technologies in the world. Western developed countries have long imposed strict technical blockades and product embargoes on China.
ZKSH relies on independent innovation and key technological breakthroughs to provide important material support for China's ability to independently develop large-scale laser devices.
The glass sheet that Hay Think team saw at ZKSH was 80 cm long and 50 cm wide, crystal clear. To talk about the special features, it is glowing with dark red inside, and the light green outer layer is tightly wrapped tightly, revealing a hint of mystery.
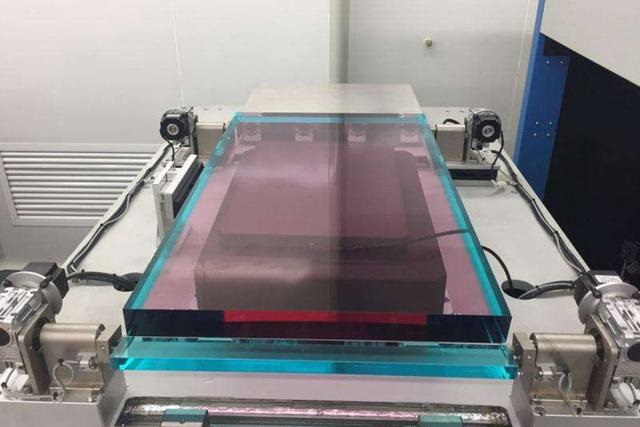
It is the famous "neodymium glass"-because it contains rare earth luminescent particles, it can generate laser light or amplify laser energy under the excitation of "pump light", and it is the "heart" of the laser.
"Seed light is a trivial laser, only nanojoule level 10-9, through thousands of large-aperture high-quality laser neodymium glass devices, it will eventually be amplified to a megajoule level 106 with the magnitude of a small sun", ZKSH high-power laser CTO Hu Lili introduced.
The performance of neodymium glass determines the potential and quality of the output energy of the laser device. After more than 10 years of continuous research, the ZKSH laser neodymium glass team has achieved a breakthrough in the key technology of large-scale laser neodymium glass mass production with continuous melting as the core, and has been successfully applied to the "Shenguang" series of devices and ultra-strong and ultra-short laser devices.
ZKSH has been engaged in the research and development of laser neodymium glass for a long time, and has successively carried out the research and development of silicate neodymium glass and phosphate laser neodymium glass. The first generation is neodymium silicate glass used in high-energy laser systems; the second generation is N21-type neodymium phosphate glass used in the high-power laser fusion system "Shenguang II Laser Experimental Device".
Since the country launched a major scientific and technological project, there has been a more urgent need for large-size high-performance laser neodymium glass.
Other Laser glass
Er Yb Glass
Er Cr Yb Glass
N31 neodymium glass
N41 neodymium glass
N51 Neodymium Glass
NAP Neodymium Glass
NF neodymium glass
NSG2 neodymium glass
SFG10 filter glass
…
"Thousands of neodymium glass components must have the same performance to ensure that 192 lasers hit the same spot at the same time to form fusion."
The United States and Japan’s HOYA and Germany’s Schott, two top international optical glass companies, completed the research and development of continuous neodymium glass smelting technology for 6 years, but they imposed strict technology and product embargoes on China. This makes independent development of batch manufacturing technology with continuous smelting technology at the core become the only solution.
Solve two major problems and master four core technologies
The neodymium glass used in laser fusion applications is phosphate glass. This kind of glass has a large expansion coefficient, strong water absorption, and serious corrosion to refractory materials and electrodes.
Therefore, continuous laser glass melting needs to overcome the technical problems of impurity control to reduce loss, dynamic removal of hydroxyl groups to meet the fluorescence lifetime index, and removal of platinum particles to achieve high laser flux, small flow and large size molding, and no burst tunnel kiln annealing series. .
In addition, in order to ensure the effective absorption of stray light, the neodymium glass needs to be encapsulated. The original hemming glue and the hemming process are prone to generate additional stress to cause the neodymium glass to break, and the light and heat radiation resistance is poor, which easily leads to the failure of the hemming.
In response to these two major problems, the research team launched targeted research and achieved breakthroughs in four key core technologies.
Through the invention of continuous smelting dynamic hydroxyl removal technology and impurity control technology, it is ensured that the hydroxyl absorption coefficient in neodymium glass reaches the international leading index;
The team invented new edging glue and edging technology, and developed batch edging mechanized equipment to achieve stable and reliable edging;
Invented the detection method of the edging residual reflection and platinum particles, which realized the full coverage of the high-efficiency and high-precision detection technology for the batch manufacturing of neodymium glass;
ZKSH has built China's first large-size phosphate laser neodymium glass continuous smelting mass production line, realizing the mass production of large-size laser neodymium glass.
The neodymium glass from the tunnel kiln needs to be cut, cooled, processed, and finally tested for its optical properties. Now the ZKSH production line can produce 1,200 pieces of large-size high-performance neodymium glass a year.
Technological innovation
The development of laser neodymium glass for half a century has condensed the efforts of three generations of Chinese scientists represented by Academician Qian Fuxi and Academician Jiang Zhonghong.

