The magnesium alloy medical device production plant of the world's leading JPBE light metal technology company has officially started production. The so-called consistent means that its research and development in magnesium alloys, production to extrusion processing, material processing, surface treatment, to the final analysis and evaluation can be completed in its own factory.
In the field of magnesium alloys in the medical field, they are the only ones in the world that do this. It also plans to manufacture a magnesium alloy bioabsorbable stent (which can be dissolved in the body and then excreted outside the body), which is known as the next-generation medical stent.
JPBE has developed high-precision microtube molding processing technology
As it is decomposed and absorbed in the body, the thickness of magnesium alloy parts will become thinner and thinner. Therefore, to achieve stable decomposition and absorption characteristics, it is necessary to achieve a uniform thickness, that is, to improve the processing accuracy, which has always been a problem. However, magnesium alloys have low plastic workability and are materials that are not easily deformed, so it is difficult to make pipes of uniform thickness by extrusion or drawing. Therefore, based on the special technology of magnesium alloy microtube extrusion processing and drawing processing method developed by JPBE, the correlation between various conditions such as extrusion temperature and drawing speed in the manufacturing process of magnesium alloy parts and the thickness was investigated. From this, the key parameters that contribute the most to the thickness accuracy can be selected, and through optimization, for the use of microtubules for medical biodegradable stents, a high-precision machining of magnesium alloys with an inner diameter of 1.5 to 3.0 mm Technology for pipes with a wall thickness of 110 to 300 μm.
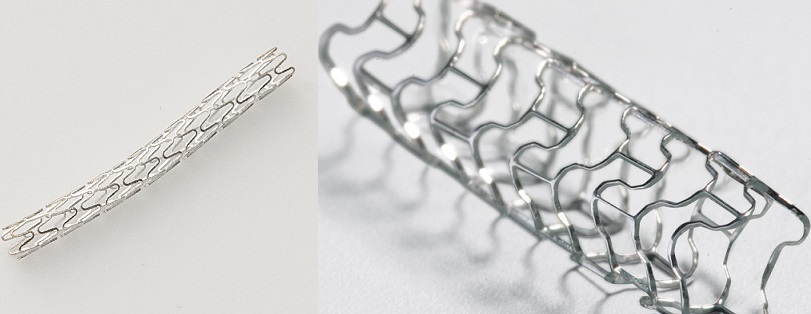
The company is currently focusing on the development of medical devices that use magnesium alloys to dissolve in the human body. After the medical stent is inserted into the narrow part and the occlusion part of the human blood vessel, it expands to restore the circulation of blood. When the blood flow returns to normal, it gradually decomposes and disappears by itself.
Mold casting equipment, extrusion processing equipment, and thin tube processing equipment were introduced into the factory. Therefore, the plant has all the processing capabilities required for the entire process from the dissolution of magnesium alloy, casting to the extrusion of thin tubes and thin wires, drawing, and finally to the final medical stent product.
In the dissolution and casting process, in order to obtain a high-quality magnesium alloy billet, it needs to be carried out in an inert gas. In the process of extruding thin tubes and thin wires, the new technology developed by the Industrial Technology Research Institute is used to completely eliminate welded wires and process wires with very high dimensional accuracy.
In the next thin tube thin wire drawing process, it is necessary to further stretch the workpiece extruded in the previous process to the required diameter and thickness. At this time, cold forging capability is the key. After this, after a series of laser processing, grinding, surface treatment, etc., finally form a bioabsorbable stent.
After the new plant is put into production, the company will develop and produce magnesium alloy medical devices in the future to meet the specifications of various magnesium alloy medical devices. Mass production technology development of various tubes, rods, wires, etc. Play a great role in promoting.

