Microcrystalline glass, also known as glass ceramics, refers to a specific composition of basic glass with or without nucleating agents. It undergoes crystallization heat treatment under a certain temperature system, uniformly precipitating a large number of tiny crystals inside the glass, forming a dense multiphase composite of microcrystalline and glass phases.
By controlling the number and size of microcrystals, transparent microcrystalline glass, microcrystalline glass with zero expansion coefficient, surface strengthened microcrystalline glass, and different colored or machinable microcrystalline glass can be obtained.
Ultra low expansion microcrystalline glass/glass ceramics
As the name suggests, ultra-low expansion microcrystalline glass has an almost zero coefficient of expansion. Under extreme cold and hot working conditions, ultra-low expansion microcrystalline glass does not crack or deform. Currently, ultra-low expansion microcrystalline glass is the material with the best dimensional stability in variable temperature environments
 |
Ultra low expansion microcrystalline glass refers to glass mainly composed of Li ₂ O, Al ₂ O, and SiO ₂, which is formed with negative expansion after strict controlled crystallization treatment β- A composite material composed of quartz solid solution nanocrystalline phase and positively expanding glass phase, with excellent optical, thermal, and mechanical properties.
The thermal expansion coefficient (0-50 ℃) of the ultra-low expansion microcrystalline glass developed by BJZC is 0 ± 0.2 × 10-6/℃.
Ultra low expansion microcrystalline glass is resistant to strong acids and alkalis
 |
Applications
In extreme environmental conditions such as mirror materials such as space cameras, photoelectric radars, astronomical telescopes…
Microcrystalline materials have a small coefficient of thermal expansion, a dense structure, and can achieve the ultimate mirror surface shape and roughness after processing. Therefore, they can be applied to multi band space camera reflectors in ultraviolet, visible and infrared…
The use of a one-time molding method to produce large-sized microcrystalline materials has a relatively short production and processing cycle, high cost-effectiveness, and low application risk, making it a type of reflective mirror material with high cost-effectiveness. Therefore, many space optical imaging systems around the world use ultra-low expansion microcrystalline materials as space reflective mirror materials.
In addition, microcrystalline glass is used as the backbone material of the core device laser gyroscope in inertial navigation systems, which can effectively prevent gas leakage in the gyroscope cavity.
The working environment temperature of the laser gyroscope varies greatly (-40~70 ℃). In order to ensure the stability of the components, it is required that the thermal expansion coefficient of the material used to manufacture the laser gyroscope cavity should be as small as possible.
The laser of the laser gyroscope is generated by the electric excitation of a mixture of helium and neon gas enclosed in the laser gyroscope cavity. To avoid helium leakage and affect the lifespan of the gyroscope, it is also required that the helium permeability of the cavity material be extremely low.
Ultra low expansion microcrystalline glass as the skeleton material of laser gyroscope
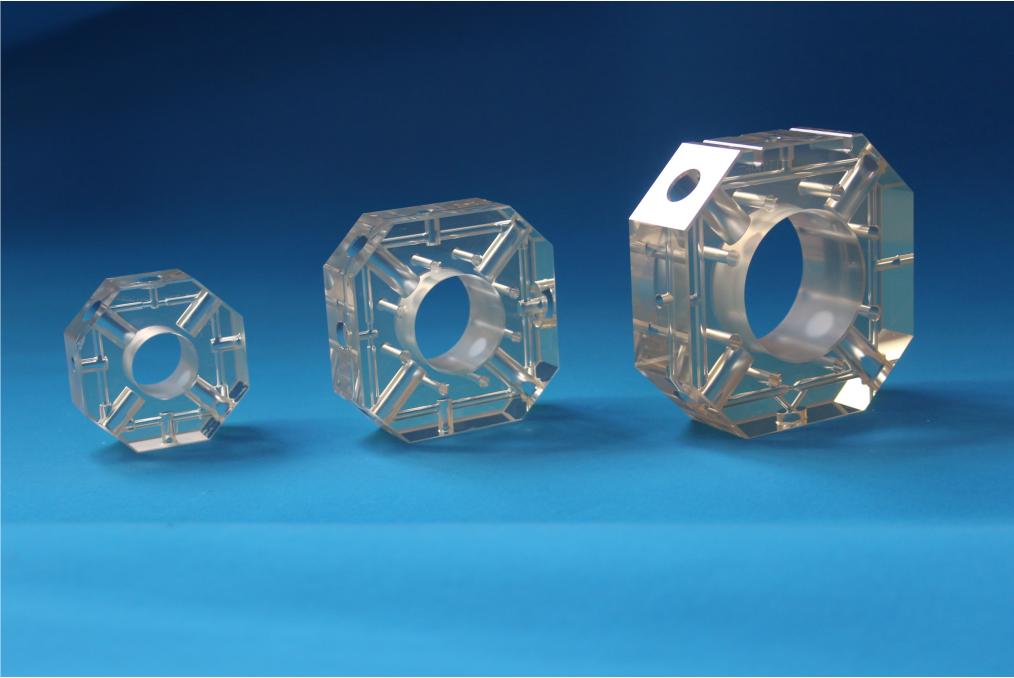 |
And ultra-low expansion microcrystalline materials are currently the materials with the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion and extremely low helium permeability. These excellent characteristics make ultra-low expansion microcrystalline materials an irreplaceable material for laser gyroscope cavities.

